Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
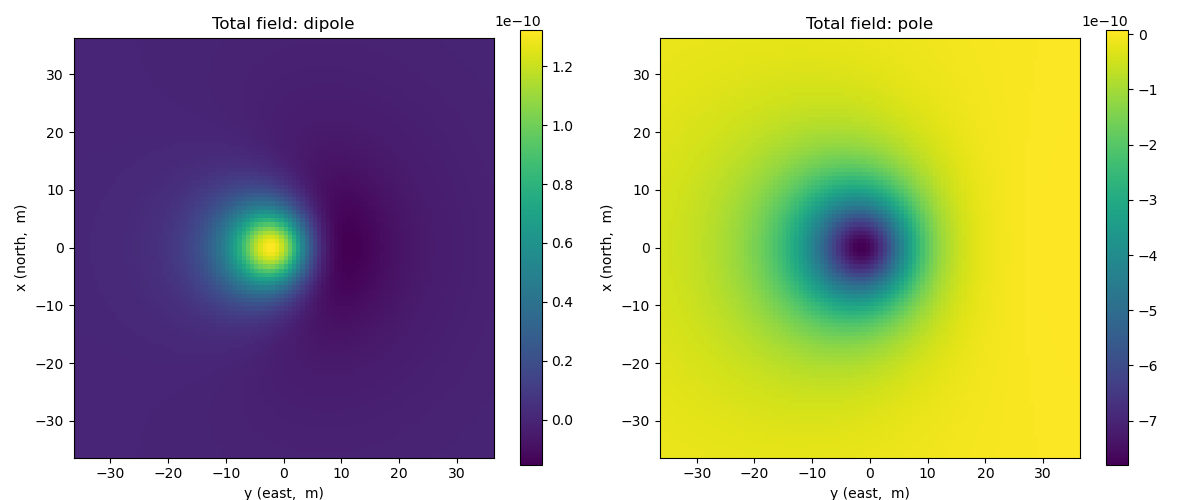
Total magnetic fields: Dipole and Pole sources#
In this example, we plot anomalous total magnetic field from a magnetic dipole and pole targets. These targets are excited by Earth magnetic fields. We can vary the direction of the Earth magnetic field, and magnetic moment of the target.
- author:
Seogi Kang (@sgkang)
- date:
Aug 19, 2018
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import LogNorm
from scipy.constants import mu_0, epsilon_0
from geoana import utils, spatial
from geoana.em import static
Setup#
define the location, orientation, and source, physical properties of the wholespace and source parameters
mu = mu_0 # permeability of free space (this is the default)
location = np.r_[0., 0., -10.] # location of the dipole or pole
# dipole parameters
moment = 1
# inclination and declination (e.g. Vancouver)
inclination, declination = 67., 0.
Magnetostatic Dipole and Loop#
Here, we build the geoana magnetic dipole and poie in a wholespace using the parameters defined above.
def id_to_cartesian(inclination, declination):
ux = np.cos(inclination/180.*np.pi)*np.sin(declination/180.*np.pi)
uy = np.cos(inclination/180.*np.pi)*np.cos(declination/180.*np.pi)
uz = -np.sin(inclination/180.*np.pi)
return np.r_[ux, uy, uz]
orientation = id_to_cartesian(inclination, declination)
dipole = static.MagneticDipoleWholeSpace(
location=location,
orientation=orientation,
moment=moment
)
pole = static.MagneticPoleWholeSpace(
location=location,
orientation=orientation,
moment=moment
)
Evaluate magnetic fields#
Next, we construct a grid where we want to plot the magentic fields and evaluate
x = np.linspace(-36, 36, 100)
y = np.linspace(-36, 36, 100)
xyz = utils.ndgrid([x, y, np.r_[1.]])
# evaluate the magnetic field
b_vec_dipole = dipole.magnetic_flux_density(xyz)
b_vec_pole = pole.magnetic_flux_density(xyz)
b_total_dipole = dipole.dot_orientation(b_vec_dipole)
b_total_pole = pole.dot_orientation(b_vec_pole)
and define plotting code to plot an image of the amplitude of the vector field / flux as well as the streamlines
def plot_amplitude(ax, v):
plt.colorbar(
ax.pcolormesh(
x, y, v.reshape(len(x), len(y), order='F')
), ax=ax
)
ax.axis('square')
ax.set_xlabel('y (east, m)')
ax.set_ylabel('x (north, m)')
Create subplots for plotting the results. Loop over frequencies and plot the electric and magnetic fields along a slice through the center of the dipole.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
# plot dipole vector potential
plot_amplitude(ax[0], b_total_dipole)
# plot loop vector potential
plot_amplitude(ax[1], b_total_pole)
# set the titles
ax[0].set_title("Total field: dipole")
ax[1].set_title("Total field: pole")
# format so text doesn't overlap
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.223 seconds)