geoana.em.tdem.ElectricDipoleWholeSpace.magnetic_field_time_deriv#
- ElectricDipoleWholeSpace.magnetic_field_time_deriv(xyz)#
Time-derivative of the magnetic field for the transient current dipole at a set of gridded locations.
For an electric current dipole oriented in the \(\hat{u}\) direction with dipole moment \(I ds\), this method computes the time-derivative of the transient magnetic field at the set of observation times for the gridded xyz locations provided.
The analytic solution is adapted from Ward and Hohmann (1988). For a transient electric current dipole oriented in the \(\hat{x}\) direction, the solution at vector distance \(\mathbf{r}\) from the current dipole is:
\[\frac{\partial \mathbf{h}}{\partial t} = - \frac{2 \, \theta^5 Ids}{\pi^{3/2} \mu \sigma} e^{-\theta^2 r^2} \big ( - z \, \mathbf{\hat y} + y \, \mathbf{\hat z} \big )\]where
\[\theta = \Bigg ( \frac{\mu\sigma}{4t} \Bigg )^{1/2}\]- Parameters:
- xyz(…, 3) numpy.ndarray
Gridded xyz locations
- Returns:
- (n_time, …, 3) numpy.ndarray of float
Time-derivative of the transient magnetic field at all times for the gridded locations provided.
Examples
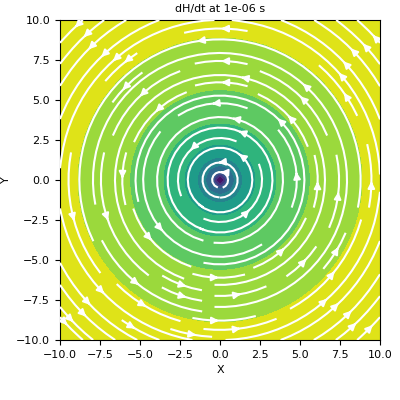
Here, we define a z-oriented electric dipole and plot the time-derivative of the magnetic field on the xy-plane that intercepts z=0.
>>> from geoana.em.tdem import ElectricDipoleWholeSpace >>> from geoana.utils import ndgrid >>> from geoana.plotting_utils import plot2Ddata >>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Let us begin by defining the electric current dipole.
>>> time = np.logspace(-6, -2, 3) >>> location = np.r_[0., 0., 0.] >>> orientation = np.r_[0., 0., 1.] >>> current = 1. >>> sigma = 1.0 >>> simulation = ElectricDipoleWholeSpace( >>> time, location=location, orientation=orientation, >>> current=current, sigma=sigma >>> )
Now we create a set of gridded locations and compute the dh/dt.
>>> xyz = ndgrid(np.linspace(-10, 10, 20), np.linspace(-10, 10, 20), np.array([0])) >>> dHdt = simulation.magnetic_field_time_deriv(xyz)
Finally, we plot dH/dt at the desired locations/times.
>>> t_ind = 0 >>> fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4)) >>> ax = fig.add_axes([0.15, 0.15, 0.8, 0.8]) >>> plot2Ddata(xyz[:, 0:2], dHdt[t_ind, :, 0:2], ax=ax, vec=True, scale='log') >>> ax.set_xlabel('X') >>> ax.set_ylabel('Y') >>> ax.set_title('dH/dt at {} s'.format(time[t_ind]))
(
Source code,png,pdf)