geoana.em.fdem.vertical_magnetic_field_horizontal_loop#
- geoana.em.fdem.vertical_magnetic_field_horizontal_loop(frequencies, sigma=1.0, mu=1.25663706127e-06, radius=1.0, current=1.0, turns=1, secondary=True)#
Vertical magnetic field at the center of a horizontal loop for each frequency
Simple function to calculate the vertical magnetic field due to a harmonic horizontal loop. The anlytic form is only available at the center of the loop.
- Parameters:
- frequenciesfloat, or numpy.ndarray
frequencies in Hz
- sigmafloat, complex, or numpy.ndarray, optional
electrical conductivity in S/m. Can provide a complex conductivity at each frequency if dispersive (i.e. induced polarization)
- mufloat, complex, or numpy.ndarray, optional
magnetic permeability in H/m. Can provide a complex permeability at each frequency if dispersive (i.e. viscous remanent magnetization)
- radiusfloat, optional
radius of the loop in meters
- current: float, optional
transmitter current in A
- turnsint, optional
number of turns for the loop source
- secondarybool, optional
if
True, the secondary field is returned. IfFalse, the total field is returned. Default isTrue
- Returns:
- complex, or numpy.ndarray
The vertical magnetic field (H/m). If secondary is
True, only the secondary field is returned. If secondary isFalse, the total field is returned.
Notes
The inputs values will be broadcasted together following normal numpy rules, and will support general shapes. Therefore every input, except for the secondary flag, can be arrays of the same shape.
The analytic expression for the total magnetic field from equation 4.94 in Ward and Hohmann 1988:
\[H_z = - \frac{I}{k^2 a^3}\left[3 - \left(3 + 3 i k a - k^2 a^2\right)e^{-i k a}\right]\]Examples
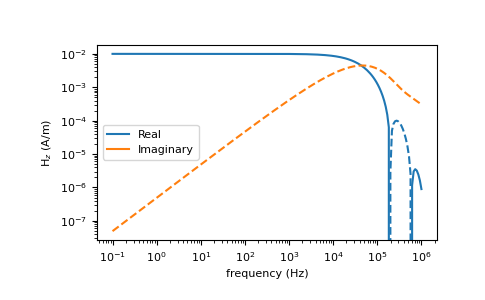
This example reproduces figure 4.7 from Ward and Hohmann
>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from geoana.em.fdem import vertical_magnetic_field_horizontal_loop
Define the frequency range,
>>> frequencies = np.logspace(-1, 6, 200) >>> hz = vertical_magnetic_field_horizontal_loop(frequencies, sigma=1E-2, radius=50, secondary=False)
Then plot the values
>>> plt.loglog(frequencies, hz.real, c='C0', label='Real') >>> plt.loglog(frequencies, -hz.real, '--', c='C0') >>> plt.loglog(frequencies, hz.imag, c='C1', label='Imaginary') >>> plt.loglog(frequencies, -hz.imag, '--', c='C1') >>> plt.xlabel('frequency (Hz)') >>> plt.ylabel('H$_z$ (A/m)') >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.show()
(
Source code,png,pdf)