geoana.em.static.ElectrostaticSphere.electric_field#
- ElectrostaticSphere.electric_field(xyz, field='all')#
Electric field for a sphere in a uniform wholespace
\[E_p(\mathbf{r}) = - \nabla V_p = \mathbf{E_0}\]- Parameters:
- xyz(…, 3) numpy.ndarray
Locations to evaluate at in units m.
- field{‘all’, ‘total’, ‘primary’, ‘secondary’}
- Returns:
- Et, Ep, Es(…, 3) np.ndarray
If field == “all”
- E(…, 3) np.ndarray
If only requesting a single field.
Examples
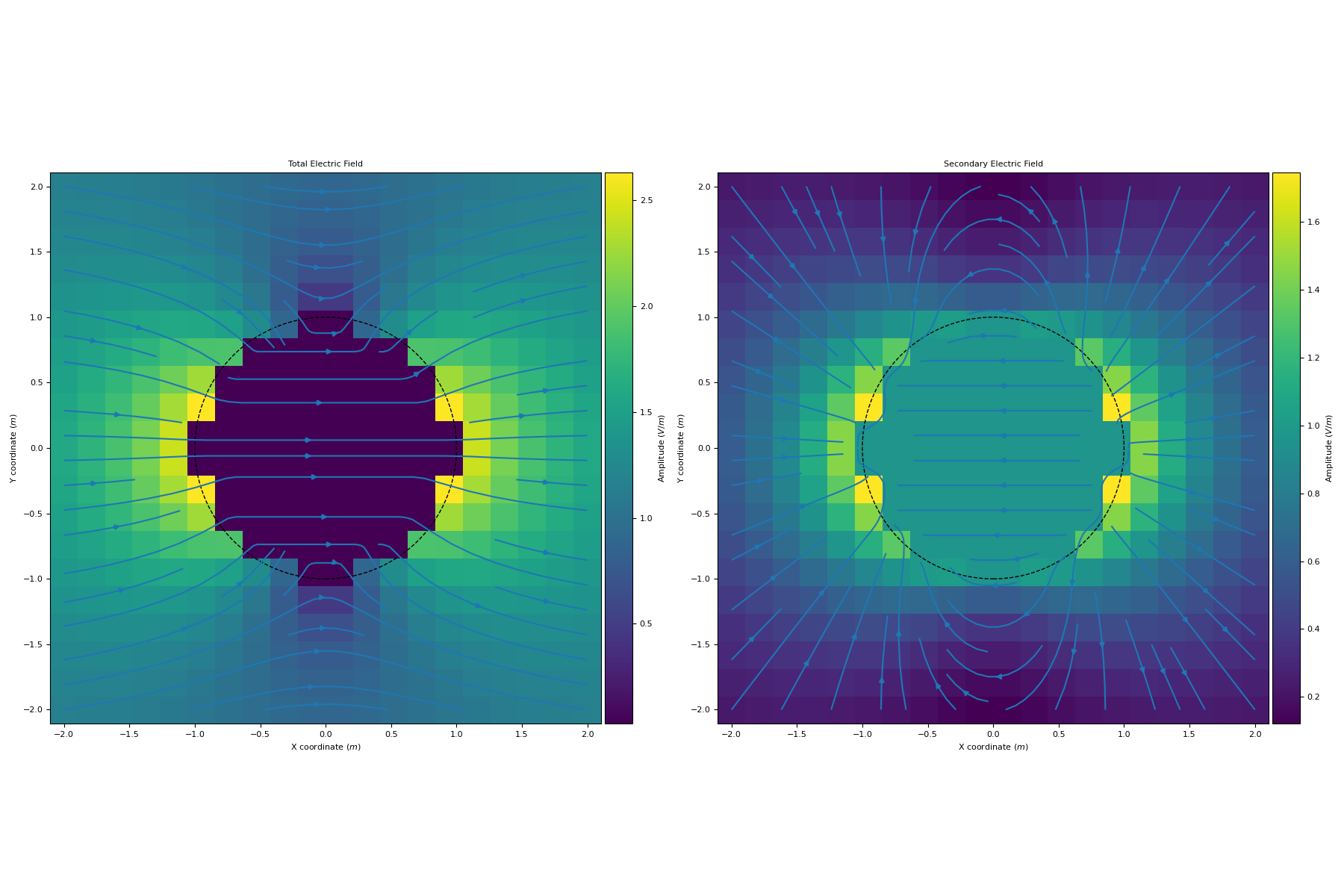
Here, we define a sphere with conductivity sigma_sphere in a uniform electrostatic field with conductivity sigma_background and plot the total and secondary electric fields.
>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from matplotlib import patches >>> from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable >>> from geoana.em.static import ElectrostaticSphere
Define the sphere.
>>> sigma_sphere = 10. ** -1 >>> sigma_background = 10. ** -3 >>> radius = 1.0 >>> simulation = ElectrostaticSphere( >>> location=None, sigma_sphere=sigma_sphere, sigma_background=sigma_background, radius=radius, primary_field=None >>> )
Now we create a set of gridded locations and compute the electric fields.
>>> X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-2*radius, 2*radius, 20), np.linspace(-2*radius, 2*radius, 20)) >>> Z = np.zeros_like(X) + 0.25 >>> xyz = np.stack((X, Y, Z), axis=-1) >>> et = simulation.electric_field(xyz, field='total') >>> es = simulation.electric_field(xyz, field='secondary')
Finally, we plot the total and secondary electric fields.
>>> fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(18,12)) >>> titles = ['Total Electric Field', 'Secondary Electric Field'] >>> for ax, E, title in zip(axs.flatten(), [et, es], titles): >>> E_amp = np.linalg.norm(E, axis=-1) >>> im = ax.pcolor(X, Y, E_amp, shading='auto') >>> divider = make_axes_locatable(ax) >>> cax = divider.append_axes("right", size="5%", pad=0.05) >>> cb = plt.colorbar(im, cax=cax) >>> cb.set_label(label= 'Amplitude ($V/m$)') >>> ax.streamplot(X, Y, E[..., 0], E[..., 1], density=0.75) >>> ax.add_patch(patches.Circle((0, 0), radius, fill=False, linestyle='--')) >>> ax.set_ylabel('Y coordinate ($m$)') >>> ax.set_xlabel('X coordinate ($m$)') >>> ax.set_aspect('equal') >>> ax.set_title(title) >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()
(
Source code,png,pdf)