geoana.em.static.LineCurrentWholeSpace.magnetic_flux_density#
- LineCurrentWholeSpace.magnetic_flux_density(xyz)#
Compute the magnetic flux density for the static current-carrying wire segments.
- Parameters:
- xyz(…, 3) numpy.ndarray xyz
gridded locations at which we are calculating the magnetic flux density
- Returns:
- (…, 3) numpy.ndarray
The magnetic flux density at each observation location in T.
Examples
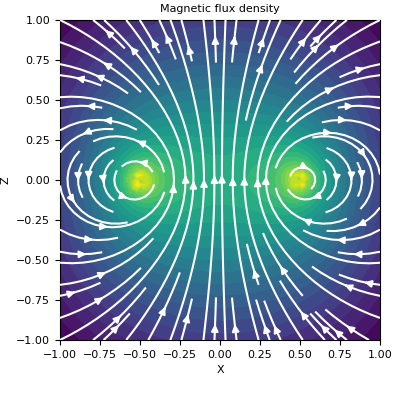
Here, we define a horizontal square loop and plot the magnetic flux density on the XZ-plane that intercepts at Y=0.
>>> from geoana.em.static import LineCurrentWholeSpace >>> from geoana.utils import ndgrid >>> from geoana.plotting_utils import plot2Ddata >>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Let us begin by defining the loop. Note that to create an inductive source, we closed the loop
>>> x_nodes = np.array([-0.5, 0.5, 0.5, -0.5, -0.5]) >>> y_nodes = np.array([-0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0.5, -0.5]) >>> z_nodes = np.zeros_like(x_nodes) >>> nodes = np.c_[x_nodes, y_nodes, z_nodes] >>> simulation = LineCurrentWholeSpace(nodes)
Now we create a set of gridded locations and compute the magnetic flux density.
>>> xyz = ndgrid(np.linspace(-1, 1, 50), np.array([0]), np.linspace(-1, 1, 50)) >>> B = simulation.magnetic_flux_density(xyz)
Finally, we plot the magnetic flux density on the plane.
>>> fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4)) >>> ax = fig.add_axes([0.15, 0.15, 0.8, 0.8]) >>> plot2Ddata(xyz[:, [0, 2]], B[:, [0, 2]], ax=ax, vec=True, scale='log', ncontour=25) >>> ax.set_xlabel('X') >>> ax.set_ylabel('Z') >>> ax.set_title('Magnetic flux density')
(
Source code,png,pdf)